Mpox (Monkeypox)
Mpox is a global public health concern and anyone can become infected.
What is Mpox?
According to the CDC, the Mpox virus is part of the same family of viruses as the variola virus, the virus that causes smallpox. Mpox symptoms are similar to smallpox symptoms but milder, and Mpox is rarely fatal. Mpox is not related to chickenpox.
What are the symptoms associated with Mpox?
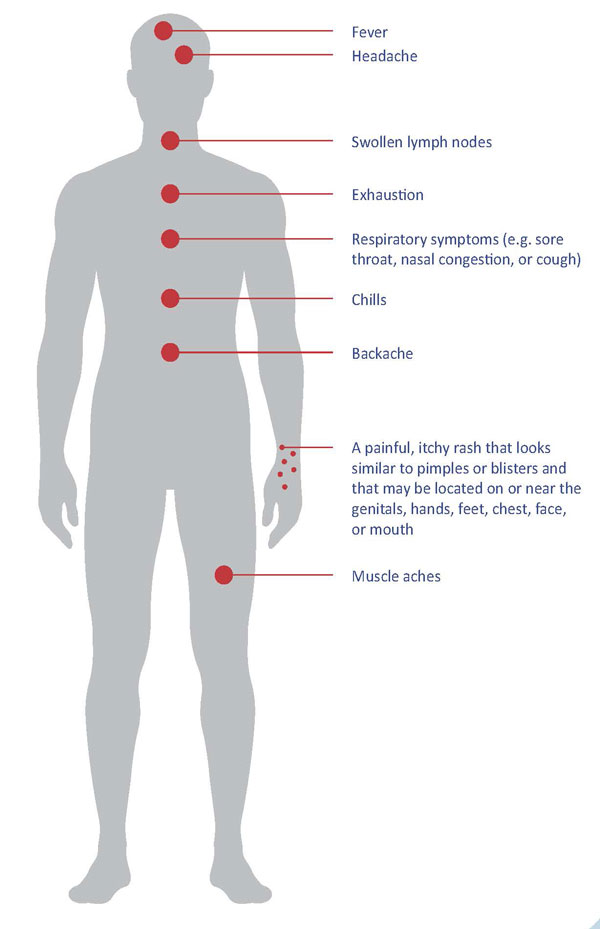
- Fever
- Headache
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Exhaustion
- Respiratory symptoms (e.g. sore
throat, nasal congestion, or cough) - Chills
- Backache
- A painful, itchy rash that looks
similar to pimples or blisters and
that may be located on or near the
genitals, hands, feet, chest, face,
or mouth - Muscle aches
What to do if you think you’re experiencing Mpox symptoms or have been exposed to Mpox:
- Seek medical care.
- Avoid close contact—including being intimate—with anyone until you can consult with a health care provider.
How does Mpox spread?
- Close, personal skin-to-skin contact.
- Direct contact with rash, scabs, or bodily fluids of someone infected with the virus.
- Touching objects or fabrics that have been used by someone with Mpox.
- Contact with the respiratory secretions of an infected individual.
Stay healthy - Mpox prevention
- Avoid close, skin-to-skin contact with people who have a rash that looks like Mpox.
- Do not touch the rash or scabs of a person with Mpox.
- Do not kiss, hug, cuddle or have sex with someone with Mpox.
- Do not share eating utensils or cups with a person with Mpox.
- Do not handle or touch the bedding, towels, or clothing of a person with Mpox.
- Practice good hand hygiene.
Resources:
Centers for Disease Control: Mpox
Texas Department of State Health Services: Mpox
